I had this issue with MYSQL 5.7 .
The following worked although it may not be ideal.
In my.cnf add:
innodb_strict_mode = 0 another way to resolve the error If InnoDB strict mode is enabled this error can show.
SET GLOBAL innodb_strict_mode=OFF; Secure file download in PHP, Security question PHP, PHP MYSQL Interview Question -Books download - PHP solutions guidelines queries update, phpmysqlquestion
I had this issue with MYSQL 5.7 .
The following worked although it may not be ideal.
In my.cnf add:
innodb_strict_mode = 0 another way to resolve the error If InnoDB strict mode is enabled this error can show.
SET GLOBAL innodb_strict_mode=OFF;
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
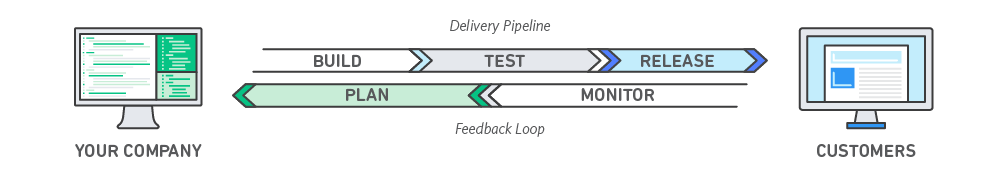
Under a DevOps model, development and operations teams are no longer “siloed.” Sometimes, these two teams are merged into a single team where the engineers work across the entire application lifecycle, from development and test to deployment to operations, and develop a range of skills not limited to a single function.
In some DevOps models, quality assurance and security teams may also become more tightly integrated with development and operations and throughout the application lifecycle. When security is the focus of everyone on a DevOps team, this is sometimes referred to as DevSecOps.
These teams use practices to automate processes that historically have been manual and slow. They use a technology stack and tooling which help them operate and evolve applications quickly and reliably. These tools also help engineers independently accomplish tasks (for example, deploying code or provisioning infrastructure) that normally would have required help from other teams, and this further increases a team’s velocity.
grep -rnE "script|link" app/Views/ | awk '!/base_url/' | awk '!/site_url/' | grep -Eo "(http|https)://[a-zA-Z0-9./?=_%:-]*" | sort -u |uniq >> url.txt
Windows tool
for creating a self-signed certificate.
https://sourceforge.net/projects/portecle/
kindly
install portecle tool from above link. The steps for creating the certificate
that we need are as given below :
1) Install
the tool from above link.
2) Go to File -> New Keystore -> PKCS #12. Click on Okay.
3) Go to Tools -> Generate Key Pair. Select RSA. Enter 2048 and click on
Okay.
4) Select SHA256 with RSA in the dropdown list. Enter roughly the details asked
in the form. Click on Okay.
5) Enter an Alias in the dialog box and click on Okay. Key Pair generation
successful message is displayed.
6) Now, right click on the keypair (identified by the alias) displayed and
click
on export.
The other opensource tool is - openSSL.
This post is about creating PKCS #12 to serve e.g. your content via HTTPS in your application itself or in another web container (such a Tomcat or another application server).
The PKCS #12 format is a binary format for storing cryptography objects. It usually contains the server certificate, any intermediate certificates (i.e. chain of trust), and the private key, all of them in a single file. A PKCS #12 file may be encrypted and signed. PKCS #12 files are usually found with the extensions .pfx and .p12.
The PKCS #12 is similar to JKS format, but you can use it not only in Java but also in other libraries in C, C++ or C# etc, so I prefer this type of a keystore to be more general.
To use PKCS #12 inside your application, you have two way how to do it:
The first option is fast and simple, but not suitable for production environment. The second option is about creating CSR to be signed by any trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
When you need to create a new certificate as quickly as possible, run the following two commands:
|
openssl – the command for executing OpenSSL.
req – certificate request and certificate generating utility in OpenSSL.
-x509 – used to generate a self-signed certificate.
-newkey rsa:4096 - option to create a new certificate request and a new private key, rsa:4096 means generating an RSA key nbits in size.
-keyout myPrivateKey.pem – use the private key file myPrivateKey.pem as the private key to combining with the certificate.
-out myCertificate.crt – use myCertificate.crt as the output certificate name.
-days 3650 – specifies the number of days to certify the certificate for.
-nodes - a created private key will not be encrypted.
|
openssl – the command for executing OpenSSL.
pkcs12 – the PKCS #12 utility in OpenSSL.
-export - the option specifies that a PKCS #12 file will be created.
-out keyStore.p12 – specifies a filename to write the PKCS #12 file to.
-inkey myPrivateKey.pem – file to read private key from.
-in myCertificate.crt – the filename to read the certificate.
The wizard will prompt you for an export password. If filled, this password will be used as a key store password.
And that is all you need, use keyStore.p12 in your application.
|
openssl – the command for executing OpenSSL.
req – certificate request and certificate generating utility in OpenSSL.
-newkey rsa:4096 - option to create a new certificate request and a new private key, rsa:4096 means generating an RSA key nbits in size.
-keyout myPrivateKey.pem – use the private key file myPrivateKey.pem as the private key to combining with the certificate.
-out request.csr – use request.csr as the certificate signing request in the PKCS #10 format.
-nodes - a created private key will not be encrypted.
|
openssl – the command for executing OpenSSL.
req – certificate request and certificate generating utility in OpenSSL.
-new - generates a new certificate request.
-key myPrivateKey.pem – specifies the file to read the private key from.
-out request.csr – use request.csr as the certificate signing request in the PKCS#10 format.
Now it is time to send request.csr as a result of the previous step to your CA (Certificate Authority) to be signed.
You are almost done. When you get a new certificate for your request.csr from your CA, use it together with a private key to create a PKCS#12 file:
|
openssl – the command for executing OpenSSL.
pkcs12 – the PKCS #12 utility in OpenSSL.
-export - the option specifies that a PKCS #12 file will be created.
-out keyStore.p12 – specifies a filename to write the PKCS #12 file to.
-inkey myPrivateKey.pem – file to read private key from.
-in myCertificate.crt – the filename to read the certificate.
-certfile CA.crt – optional parameter to read additional certificates from, useful to create a complete trust chain.
The output file keyStore.p12 is what you need to add to your application. When you filled an export password use it as a key store password in a configuration file.
I had this issue with MYSQL 5.7 . The following worked althoug...